| Class of Coldness | Light Condition | ||
| Class of Warmness | Class of Soil | ||
| Preference of Soil | |||
| Requirement of Shading | |||
| Figure | 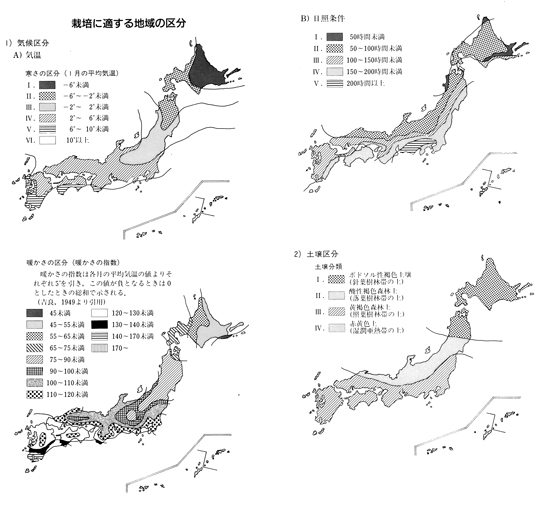 | ||
Plant data
| Latin name | Glehnia littoralis Fr. Schmidt ex Miquel | |||||||||
| Family name | Umbelliferae | |||||||||
| Common name | ||||||||||
| Cultivar | ||||||||||
| Classification | ||||||||||
| Photo |

| |||||||||
| Characteristics | ||||||||||
| Habitat | ||||||||||
Growing data
 | ||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Photo library | Photo library | |||||||||
Reference
 | ||||||||||
|
Hata, K. et al., Stimulating activity of F-gitonin, a steroidal saponin from Hosta sieboldiana on human neutrophils-like cells. Natural Medicines (2002), 56(4), 153-156. Ishikawa, T. et al., Water-soluble constituents of Glehnia littoralis fruit. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (2001), 49(5), 584-588. Nakano, Y. et al., Antiproliferative constituents in Umbelliferae plants. II. Screening for polyacetylenes in some Umbelliferae plants, and isolation of panaxynol and falcarindiol from the root of Heracleum moellendorffii. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1998), 21(3), 257-261. Matsuura, H. et al., Antibacterial and antifungal polyyne compounds from Glehnia littoralis. Planta Medica (1996), 62(3), 256-259. Sasaki, H. et al., The constituents of Glehnia littoralis Fr. Schmidt et Miq. Structure of a new coumarin glycoside, osthenol-7-O-β -gentiobioside. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1980), 28(6), 1847-52. | ||||||||||
| Crude drug | ||||||||||
| Cultured tissue and efficient propagation | ||||||||||
| Plant culture and efficient production method | ||||||||||
| Sakuyo hyohon | ||||||||||
| Transcriptome, Genomics etc. | ||||||||||
| Red list data | ||||||||||
| Resource data |
| |||||||||