| Class of Coldness | I~III | Light Condition | II~IV |
| Class of Warmness | 45~100 | Class of Soil | I~III |
| Preference of Soil | |||
| Requirement of Shading | |||
| Figure | 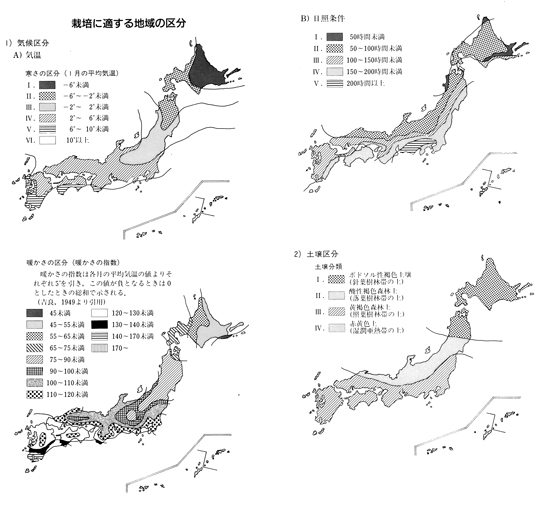 | ||
Plant data
| Latin name | Carthamus tinctorius L. | |||||||||
| Family name | Compositae | |||||||||
| Common name | Safflower | |||||||||
| Cultivar | ||||||||||
| Classification | ||||||||||
| Photo |

| |||||||||
| Characteristics | ||||||||||
| Habitat | ||||||||||
Growing data
 | ||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Photo library | Photo library | |||||||||
Reference
 | ||||||||||
|
Li, F. et al., Flavonoids from Carthamus tinctorius. Chinese Journal of Chemistry (2002), 20(7), 699-702. Yin, H. et al., Studies on chemical constituents of Carthamus tinctorius. Zhongcaoyao (2001), 32(9), 776-778. Kazuma, K. et al., Quinochalcones and flavonoids from fresh florets in different cultivars of Carthamus tinctorius L. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry (2000), 64(8), 1588-1599. Ahmed, K. M. et al., A new flavone diglycoside from Carthamus tinctorius seeds. Pharmazie (2000), 55(8), 621-622. Yin, H.-B. et al., Cartorimine, a new cycloheptenone oxide derivative from Carthamus tinctorius. Journal of Natural Products (2000), 63(8), 1164-1165. Yin, H.-B. et al., A novel semi-quinone chalcone sharing a pyrrole ring C-glycoside from Carthamus tinctorius. Tetrahedron Letters (2000), 41(12), 1955-1958. Tsunajima, F. et al., Isolation and chemical structure of precarthamin from the fresh petal of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Journal of Advanced Science (1997), 9(1&2), 106-107. Goda, Y. et al., Structure of safflomin A and content of safflomin I (safflor yellow) in commercial safflower yellow products. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Gakkaishi (1997), 4(1), 54-58. Kim, J.-B. et al., Purification and structural identification of carthamin from Carthamus tinctorius. Han'guk Nonghwa Hakhoechi (1996), 39(6), 501-505. Zhang, H. L. et al., Novel antioxidants from safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) oil cake. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1996), 44(4), 874-6. Kumazawa, T. et al., Precursor of carthamin, a constituent of safflower. Chemistry Letters (1994), (12), 2343-4. Akihisa, T. et al., Erythro-hentriacontane-6,8-diol and 11 other alkane-6,8-diols from Carthamus tinctorius. Phytochemistry (1994), 36(1), 105-8. Meselhy, M. R. et al., Two new quinochalcone yellow pigments from Carthamus tinctorius and Ca2+ antagonistic activity of tinctormine. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1993), 41(10), 1796-802. Meselhy, M. R. et al., Tinctormine, a novel calcium antagonist N-containing quinochalcone C-glycoside from Carthamus tinctorius L. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1992), 40(12), 3355-7. Hattori, M. et al., 6-Hydroxykaempferol and its glycosides from Carthamus tinctorius petals. Phytochemistry (1992), 31(11), 4001-4. Onodera, J. et al., The structure of safflomin C, a constituent of safflower. Chemistry Letters (1989), (9), 1571-4. Sato, H. et al., Serotobenine, a novel phenolic amide from safflower seeds (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Agricultural and Biological Chemistry (1985), 49(10), 2969-74. | ||||||||||
| Crude drug | CARTHAMI FLOS | |||||||||
| Cultured tissue and efficient propagation | ||||||||||
| Plant culture and efficient production method | Plant culture | |||||||||
| Sakuyo hyohon | ||||||||||
| Transcriptome, Genomics etc. | ||||||||||
| Red list data | ||||||||||
| Resource data |
| |||||||||