| 寒さの区分 | I~III | 日照条件 | II~IV |
| 暖かさの区分 | 45~100 | 土壌分類 | I~III |
| 土壌適正 | 排水の良い場所に適する. 火山灰土,沖積土に適する.肥沃地に適する. | ||
| 遮光 | 不要 | ||
| 画像 | 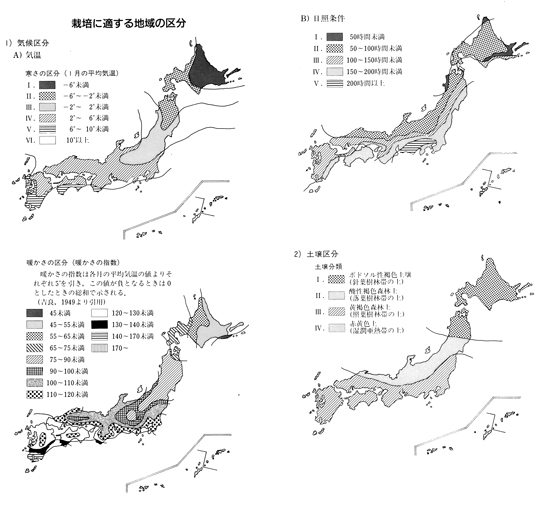 | ||
植物詳細
| 植物名 | ベニバナ | |||||||||
| ラテン名 | Carthamus tinctorius L. | |||||||||
| 科名 | Compositae | |||||||||
| 和科名 | キク科 | |||||||||
| 一般名 | ベニバナ | |||||||||
| 一般英名 | Safflower | |||||||||
| 品種等 | もがみ | |||||||||
| 分類 | 1〜2年生草本 | |||||||||
| 画像 |

| |||||||||
| 形態的特徴 | 高さ1m内外に達する.葉は互生し長だ円形~広皮針形で,大小不同の鋸歯があり,先は鋭い剌となる.全株無毛である.6~7月,頭花を頂生する.総苞外片には鋭い剌がある.花は管状花のみで,先が深く5裂し,咲き始めは鮮黄色で,次第に紅黄色になる.痩果は長さ7mm,帯白色で光沢があり,冠毛は鱗片状で,脱落しやすい. もがみべにばなは草丈が在来種に比べてやや高く,茎の色も緑色がやや濃い.ともに葉の縁は剌状になる.花はもがみべにばなの頭花はやや大きく,頭花の小花数は60~80個,開花盛期の花色は橙赤色に対して,在来種はやや小さく,小花数は50~65個,花色は黄色から橙色である. | |||||||||
| 生態的特徴 | 耐寒性が強く,耐暑性,耐湿性,耐酸性は弱い. | |||||||||
生育特性  | ||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| 写真ライブラリー | 写真ライブラリー | |||||||||
文献情報  | ||||||||||
|
Li, F. et al., Flavonoids from Carthamus tinctorius. Chinese Journal of Chemistry (2002), 20(7), 699-702. Yin, H. et al., Studies on chemical constituents of Carthamus tinctorius. Zhongcaoyao (2001), 32(9), 776-778. Kazuma, K. et al., Quinochalcones and flavonoids from fresh florets in different cultivars of Carthamus tinctorius L. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry (2000), 64(8), 1588-1599. Ahmed, K. M. et al., A new flavone diglycoside from Carthamus tinctorius seeds. Pharmazie (2000), 55(8), 621-622. Yin, H.-B. et al., Cartorimine, a new cycloheptenone oxide derivative from Carthamus tinctorius. Journal of Natural Products (2000), 63(8), 1164-1165. Yin, H.-B. et al., A novel semi-quinone chalcone sharing a pyrrole ring C-glycoside from Carthamus tinctorius. Tetrahedron Letters (2000), 41(12), 1955-1958. Tsunajima, F. et al., Isolation and chemical structure of precarthamin from the fresh petal of safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Journal of Advanced Science (1997), 9(1&2), 106-107. Goda, Y. et al., Structure of safflomin A and content of safflomin I (safflor yellow) in commercial safflower yellow products. Nippon Shokuhin Kagaku Gakkaishi (1997), 4(1), 54-58. Kim, J.-B. et al., Purification and structural identification of carthamin from Carthamus tinctorius. Han'guk Nonghwa Hakhoechi (1996), 39(6), 501-505. Zhang, H. L. et al., Novel antioxidants from safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.) oil cake. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1996), 44(4), 874-6. Kumazawa, T. et al., Precursor of carthamin, a constituent of safflower. Chemistry Letters (1994), (12), 2343-4. Akihisa, T. et al., Erythro-hentriacontane-6,8-diol and 11 other alkane-6,8-diols from Carthamus tinctorius. Phytochemistry (1994), 36(1), 105-8. Meselhy, M. R. et al., Two new quinochalcone yellow pigments from Carthamus tinctorius and Ca2+ antagonistic activity of tinctormine. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1993), 41(10), 1796-802. Meselhy, M. R. et al., Tinctormine, a novel calcium antagonist N-containing quinochalcone C-glycoside from Carthamus tinctorius L. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1992), 40(12), 3355-7. Hattori, M. et al., 6-Hydroxykaempferol and its glycosides from Carthamus tinctorius petals. Phytochemistry (1992), 31(11), 4001-4. Onodera, J. et al., The structure of safflomin C, a constituent of safflower. Chemistry Letters (1989), (9), 1571-4. Sato, H. et al., Serotobenine, a novel phenolic amide from safflower seeds (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Agricultural and Biological Chemistry (1985), 49(10), 2969-74. | ||||||||||
| 生薬名 | コウカ | |||||||||
| 組織培養物及び効率的増殖法 | ||||||||||
| 植物体栽培及び植物の効率的生産法 | 栽培情報 | |||||||||
| さく葉標本情報 | ||||||||||
| トランスクリプトーム・ゲノミクス情報 | ||||||||||
| 稀少植物情報 | ||||||||||
| 保有資源情報 |
| |||||||||