| Class of Coldness | II~V | Light Condition | II~IV |
| Class of Warmness | 65~120 | Class of Soil | II, III |
| Preference of Soil | |||
| Requirement of Shading | |||
| Figure | 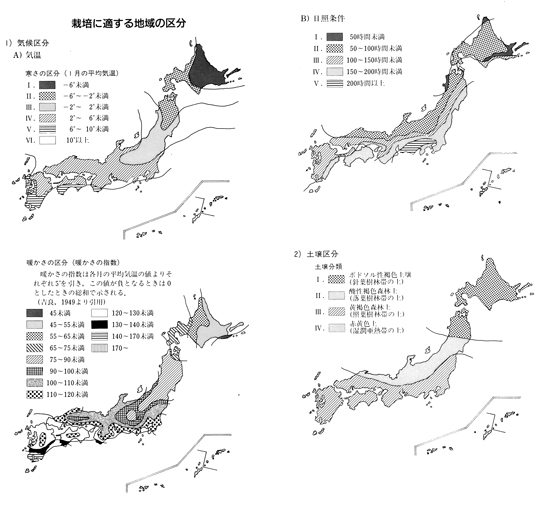 | ||
Plant data
| Latin name | Rehmannia glutiosa Libosch. f. hueichingensis (Chao et Schih) Hsiao | |||||||||
| Family name | Scrophulariaceae | |||||||||
| Common name | Chinese foxglove | |||||||||
| Cultivar | ||||||||||
| Classification | ||||||||||
| Photo |

| |||||||||
| Characteristics | ||||||||||
| Habitat | ||||||||||
Growing data
 | ||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||
| Photo library | Photo library | |||||||||
Reference
 | ||||||||||
|
Matsuda, H. et al., Studies on Rehmanniae Radix. V. 5-Hydroxymethyl-2-furaldehyde, active constituent of the steamed root of Rehmannia glutinosa having increasing activity of erythrocyte deformability in rats. Natural Medicines (2004), 58(1), 34-37. Kitagawa, I. et al., On the constituents of the root of Fukuchiyama-jio, the hybrid of Rehmannia glutinosa var. purpurea and R. glutinosa forma hueichingensis. Yakugaku Zasshi (1998), 118(10), 464-475. Kubo, M. et al., Rehmanniae Radix. III. The relation between changes of constituents and improvable effects on hemorheology with the processing of roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Yakugaku Zasshi (1996), 116(2), 158-68. Yoshikawa, M. et al., Chemical studies on crude drug processing. IX. On the constituents of Rehmanniae Radix. (3). Absolute stereo-structures of rehmaionosides A, B, and C, and rehmapicroside, biologically active ionone glucosides and a monoterpene glucoside isolated from Chinese Rehmanniae Radix. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1996), 44(1), 41-7. Kitagawa, I. et al., Chemical studies on crude drug processing. X. On the constituents of Rehmanniae Radix (4): comparison of the constituents of various Rehmanniae Radixes originating in China, Korea, and Japan. Yakugaku Zasshi (1995), 115(12), 992-1003. Kitagawa, I. et al., Chemical studies on crude drug processing. VIII. On the constituents of Rehmanniae Radix. (2): absolute stereostructures of rehmaglutin C and glutinoside isolated from Chinese Rehmanniae Radix, the dried root of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1995), 43(7), 1096-100. Kitagawa, I. et al., Chemical studies on crude drug processing. VII. On the constituents of Rehmanniae radix. (1): Absolute stereostructures of Rehmaglutins A, B, and D isolated from Chinese rehmanniae radix, the dried root of Rehmannia glutinosa Libosch. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1991), 39(5), 1171-6. Ni, M. et al., Constituents of the dry roots of Rehmannia glutinosa. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi (1992), 17(5), 297-8. Seto, T. et al., Studies on the bioactive constituents in Jio (Dihuang). (I). Isolation of a suppressive component for the guinea pig heart function from Kanjio (Gandihuang). Wakan Iyaku Gakkaishi (1991), 8(2), 115-24. Wu, S. et al., Studies on the chemical constituents of Huaiqing rehmannia (Rehmannia glutinosa f. hueichingenesis). Zhongcaoyao (1984), 15(7), 294-6. Tomoda, M. et al., Water-soluble constituents of Rehmannia radix. II. Constituents of roots of Rehmannia glutinosa var purpurea. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1971), 19(11), 2411-13. Tomoda, M. et al., Water-soluble constituents of Rehmanniae radix. I. Carbohydrates and acids of Rehmannia glutinosa f. hueichingensis. Chemical & Pharmaceutical Bulletin (1971), 19(7), 1455-60. Kitagawa, I. et al., Constituents of rhizome of Rehmannia glutinosa f. hueichingensis. Yakugaku Zasshi (1971), 91(5), 593-6. | ||||||||||
| Crude drug | REHMANNIAE RADIX | |||||||||
| Cultured tissue and efficient propagation |
Rehmannia_glutinosa_f._hueichingensis-Ref-1
,
Rehmannia_glutinosa_f._hueichingensis-Ref-2
,
Rehmannia_glutinosa-Rep-1
| |||||||||
| Plant culture and efficient production method | Plant culture | |||||||||
| Sakuyo hyohon | Herbarium | |||||||||
| Transcriptome, Genomics etc. | ||||||||||
| Red list data | ||||||||||
| Resource data |
| |||||||||