| 寒さの区分 | II~IV | 日照条件 | II~IV |
| 暖かさの区分 | 75~120 | 土壌分類 | II~III |
| 土壌適正 | 排水及び保水の良い場所に適する.砂質壌土~埴質壌土に適する.肥沃地に適する. | ||
| 遮光 | 必要 | ||
| 画像 | 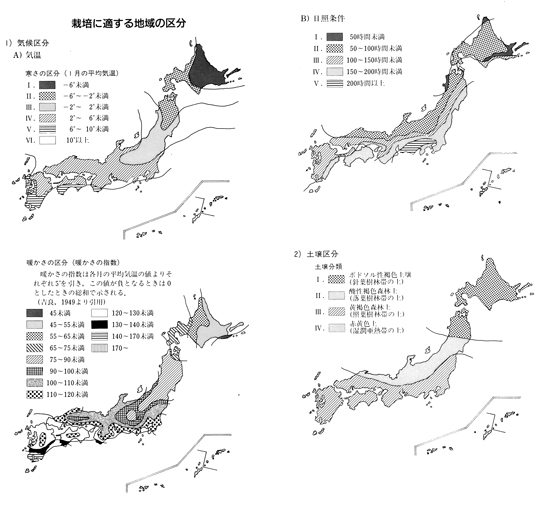 | ||
植物詳細
| 植物名 | オタネニンジン | ||||||||||||
| ラテン名 | Panax ginseng C. A. Mey. | ||||||||||||
| 科名 | Araliaceae | ||||||||||||
| 和科名 | ウコギ科 | ||||||||||||
| 一般名 | オタネニンジン | ||||||||||||
| 一般英名 | Ginseng | ||||||||||||
| 品種等 | みまき | ||||||||||||
| 分類 | 多年生草本 | ||||||||||||
| 画像 |

| ||||||||||||
| 形態的特徴 | 栽培植物の根茎は短く,主根は肥大して分枝する.茎は直立し,単一で無毛,頂部にほぼ1葉ずつ年ごとに増す葉を輪生する.この葉は掌状複葉で,葉柄は葉身とほぼ等長,小葉は5~7枚(初生葉は3枚)で頂片が最も大きく,各片は倒卵形~倒皮針形,葉先は尖り,やや膜質,小葉柄の長さは1~2cmである.茎頂から花茎を出し,散形花序に淡黄緑色の小花を多数付ける.液果は直径5~9mmで,成熟すると鮮紅色となり,内部に半円形の枝果2個がある.現在栽培されているものは,茎葉を詳細に観察すると種々雑多な混系である.しかし,根の形状は胴(主根)及び脚(支根)か長く,分枝性が強く,直播きの場合もほぼ同様である. | ||||||||||||
| 生態的特徴 | ロシアの沿海州,中国東北部,朝鮮半島原産の多年生草本.花期4~7月.通常,寒冷な気候を好む.国内における主な栽培地は長野県,福島県で,島根県の大根島でも若干の栽培が行われている.栽培地の標高は400~800mの間といわれているが,島根県の大根島の標高は20~30mであり,他の主産地に比較して高温・多雨の条件下で栽培されている.これらのことより考えると,局地的には不適地があるとしても,極めて順応性の高い植物である.土性は砂質壌土から埴質壌土がよいとされ,pHは4.5~5.8の弱酸性によく生育する.国外の産地は,中国(吉林省,黒竜江省,遼寧省),韓国,北朝鮮 | ||||||||||||
生育特性  | |||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||
| 写真ライブラリー | 写真ライブラリー | ||||||||||||
文献情報  | |||||||||||||
|
Hirakura, K. et al., The constituents of Panax ginseng. Part 4. Linoleoylated polyacetylenes from the root of Panax ginseng. Phytochemistry (1994), 35(4), 963-7. Hirakura, K. et al., The constituents of Panax ginseng. Part 2. Three acetylated polyacetylenes from the roots of Panax ginseng. Phytochemistry (1991), 30(12), 4053-5. Hirakura, K. et al., The constituents of Panax ginseng. Part 3. Three acetylenic compounds from roots of Panax ginseng. Phytochemistry (1992), 31(3), 899-903. Park, J. D. et al., A thiazole and two β -carboline constituents from Panax ginseng. Archives of Pharmacal Research (1988), 11(1), 52-5. Xu, S. et al., Chemical constituents of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer 13. Saponins of sarcocarp in the Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Shenyang Yaoxueyuan Xuebao (1988), 5(1), 59. Kitagawa, I. et al., Chemical studies on crude drug processing. V. On the constituents of ginseng radix rubra (2): comparison of the constituents of white ginseng and red ginseng prepared from the same Panax ginseng root. Yakugaku Zasshi (1987), 107(7), 495-505. Wang, Z. et al., Flavonoid constituents of the stems and leaves of Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer. Shenyang Yaoxueyuan Xuebao (1985), 2(4), 284-7. Lu, Y. et al., Chemical constituents of ginseng. 5. Isolation and identification of steroid-saponins and triterpene-saponins of ginseng. Shenyang Yaoxueyuan Xuebao (1985), 2(3), 177-84. Iwabuchi, H. et al., Studies on the aroma constituents of crude drugs. I. On the aroma constituents of Ginseng radix. Yakugaku Zasshi (1984), 104(9), 951-8. Tanaka, O., Chemical constituents of ginseng. Taisha (1973), 10(5), 548-55. Komatsu, M. et al., Constituents of the herb of Panax ginseng. II. Flavonoid constituents. Yakugaku Zasshi (1969), 89(1), 122-6. Shibata, S. et al., Structure of panaxadiol, a saponin of ginseng. Tetrahedron Letters (1962), 419-22. | |||||||||||||
| 生薬名 |
ニンジン
コウジン | ||||||||||||
| 組織培養物及び効率的増殖法 |
Panax_ginseng-Ref-1
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-2
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-3
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-4
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-5
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-6
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-7
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-8
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-9
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-10
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-11
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-12
,
Panax_ginseng-Ref-13
| ||||||||||||
| 植物体栽培及び植物の効率的生産法 | 栽培情報 | ||||||||||||
| さく葉標本情報 | さく葉標本 | ||||||||||||
| トランスクリプトーム・ゲノミクス情報 | |||||||||||||
| 稀少植物情報 | |||||||||||||
| 保有資源情報 |
| ||||||||||||